Thyroid Eye Disease
General Information
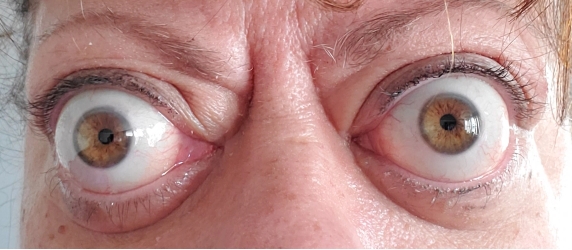
• Thyroid eye disease is an autoimmune disease that affects the tissues around the eye, most commonly developing in association with Graves’ disease.
• It can present with forward protrusion of the eyes, lid retraction, redness, swelling, and sometimes double vision.
• The disease progresses in two phases: active and inactive.
Treatment Methods
• Treatment plan is determined according to the stage of the disease.
• In mild cases, artificial tears and protective measures may be sufficient.
• Medical treatments aimed at suppressing inflammation can be applied in the active phase.
• Surgical treatments can be planned in the inactive phase if there are permanent findings.
Recovery Process
• The course of the disease varies from person to person.
• Surgical results become more stable after the active phase is brought under control.
• The treatment process can be long-term and requires regular follow-up.
Advantages
• Visual function can be preserved with treatments applied at the correct stage.
• Complaints of eye protrusion, lid retraction, and double vision can be reduced.
• Significant improvement can be achieved both functionally and aesthetically.
Limitations
• The disease cannot be completely eliminated, it is controlled.
• The treatment process can take time and requires patience.
• Multiple surgical interventions may be needed in some patients.
• Results may vary depending on personal anatomy and disease severity.
Orbital Decompression
General Information
• Orbital decompression is a surgical procedure that aims to reduce the forward protrusion of the eye by controlled reduction of bone and/or fat tissue behind the eyeball.
• It is most commonly applied in thyroid eye disease in cases that threaten vision or eyelid closure.
• It can also provide aesthetic improvement in addition to functional necessities.
Treatment Methods
• Bone decompression, fat decompression, or combined methods can be preferred according to the patient’s findings.
• Surgical planning is personalized according to the degree of eye protrusion, risk of double vision, and orbital anatomy.
• Can be planned together with a multidisciplinary approach (ENT, endocrinology) when needed.
Recovery Process
• Significant edema and bruising may be seen in the first days after surgery.
• Swelling usually gradually decreases within weeks.
• Final results may take a few months to appear.
• Regular follow-ups are important for the healthy progression of the healing process.
Advantages
• Forward protrusion of the eyeball can be reduced.
• Pressure on the optic nerve can be relieved.
• Eyelid closure problems and corneal dryness can decrease.
• Can provide significant relief both functionally and aesthetically.
Limitations
• The same degree of regression may not be achieved in every patient.
• Risk of double vision may occur or increase in some patients.
• Multiple surgical stages may be needed.
• The healing process requires patience and close follow-up.